Model Dev & Offline Eval
Model dev & training
Ensembles
- bagging:
good with unstable methods
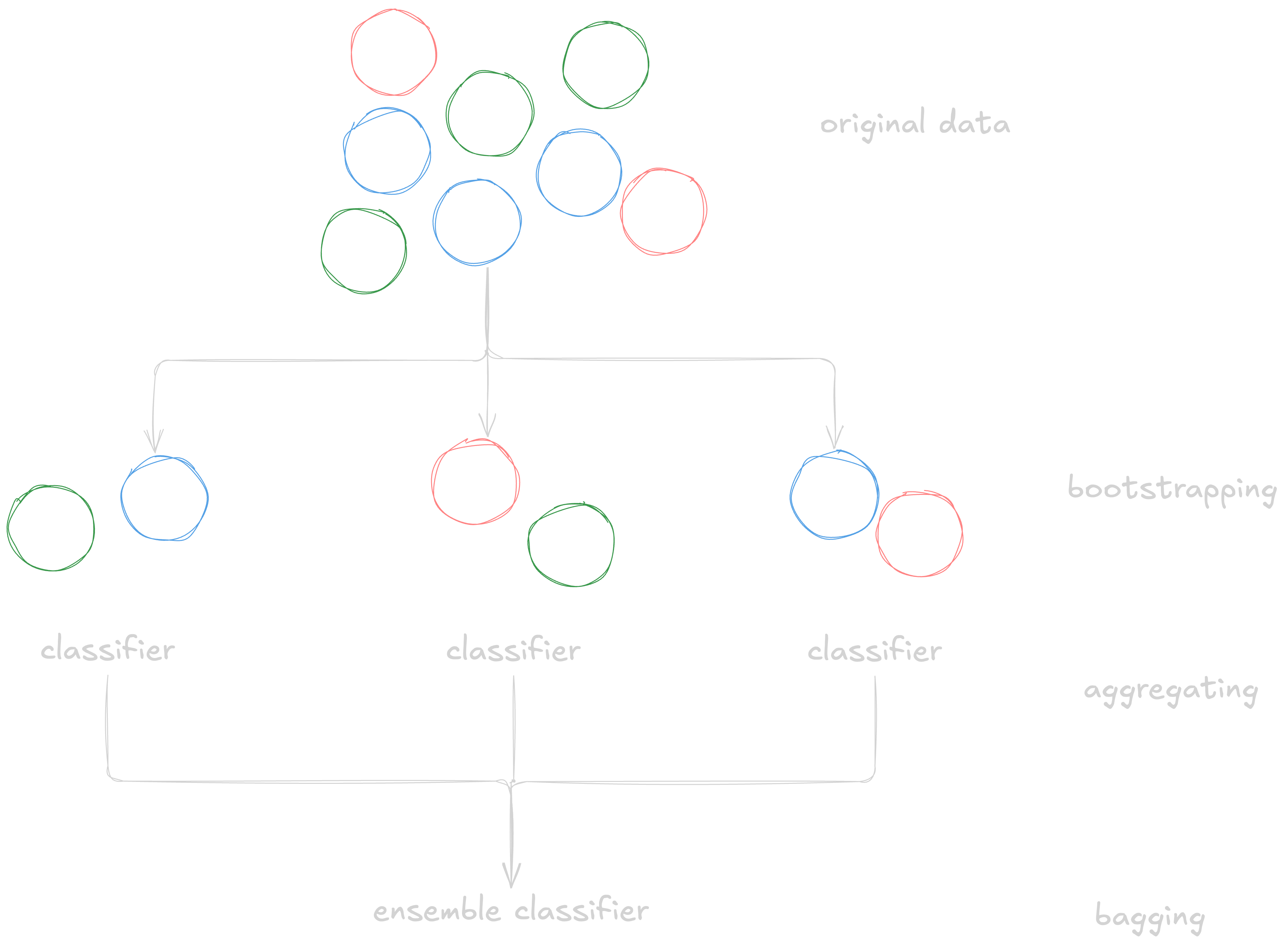
- boosting
- stacking
Experiment Tracking & Versionning
MLFlow Keep track of at least:
- speed
- system performance metrics
- values of params & hyperparams over time
- loss curve
- model performance metrics
- log of corresponding sample, prediction & ground truth label
Distributed Training
- data parallelism : how to accurately and effectively accumulate gradients from different machines
- Synchronous SGD : Synchronous Stochastic Gradient Descent
- ASGD : Asynchronous Stochastic Gradient Descent ASGD converges but requires more step than Synchronous SGD, but generaly, gradient updates are sparse, so gradient staleness is less of a problem & the two converges similarly.
Model Evaluation
essential to know the baseline your evaluating against the model -Random baseline if model predict at random, what’s the expected performance ?
[!example] data set with 90 negatives and 10 positives observations
random distribution Accuracy F1 Uniform random (0.5) 0.5 0.167 Task label distribution 0.82 0.1
- Simple heuristics
- Zero rule baseline: special case of simple heuristics : always predict the common class
- Human baseline
- Existing solutions
Evaluating Methods
- perturbation tests
- invariance tests
- directional expectation tests
- model calibration : allow to interpret the output of a model as a probability. Often, model calibration is critical for models in production that are being improved through continual learning and feedback.
- confidence measurement
- slice based evaluation :
- minority
- critical subgroup
- simpson paradox : a trend appears in several subgroups but it’s reversed when combined.
- track model performances on critical slices:
- heuristics based slices
- error analysis slice
- slice finder