Data Engineering Fundamentals
Data Sources
- input data : generally comes from user, can be dirty
- system generated data : includes various types of logs and systems output.
Caution
- logs are noizy -> hard to find signal (Logstash, Datadog, Log2.io)
- store large amount of data -> low-access / high-frequency access storage
- intern data base
- thrid party data
Data Formats
==data serialization== : process of converting a data structure into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later. Wikipedia
Row-Major VS Column-Major Format
row-major -> [[Contiguous data]] makes it faster to read and write data observations (Numpy) column-major -> better for analysis purposes ([[Pandas Python]])
Data Models
Relational Models
- unordered data : order of the rows/columns is not important
relations should be normalized (1FN, 2FN, etc…), it will help to reduce the redudancy & improve data integrity
[!caution] One major downside is that data can be massively spreaded and it can be costfull to run jointure operations
NoSQL Models
- a document database :
- better locality, so easier to retrieve information
- harder to join
- a graph database:
- based on relations
Structured VS Unstuctured Data
| Structured Data | Unstructured Data | | ————— | —————– | | Data Warehouse | Data Lake |
Data Storage Engines & Processing
Transactionnal VS Analytical Processing
- OLTP (Online Transactionnal Processing)
- OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)
Modes of Dataflow
- Data passing through databases
- Data passing through services
- Microservice architecture (==request-driven==)
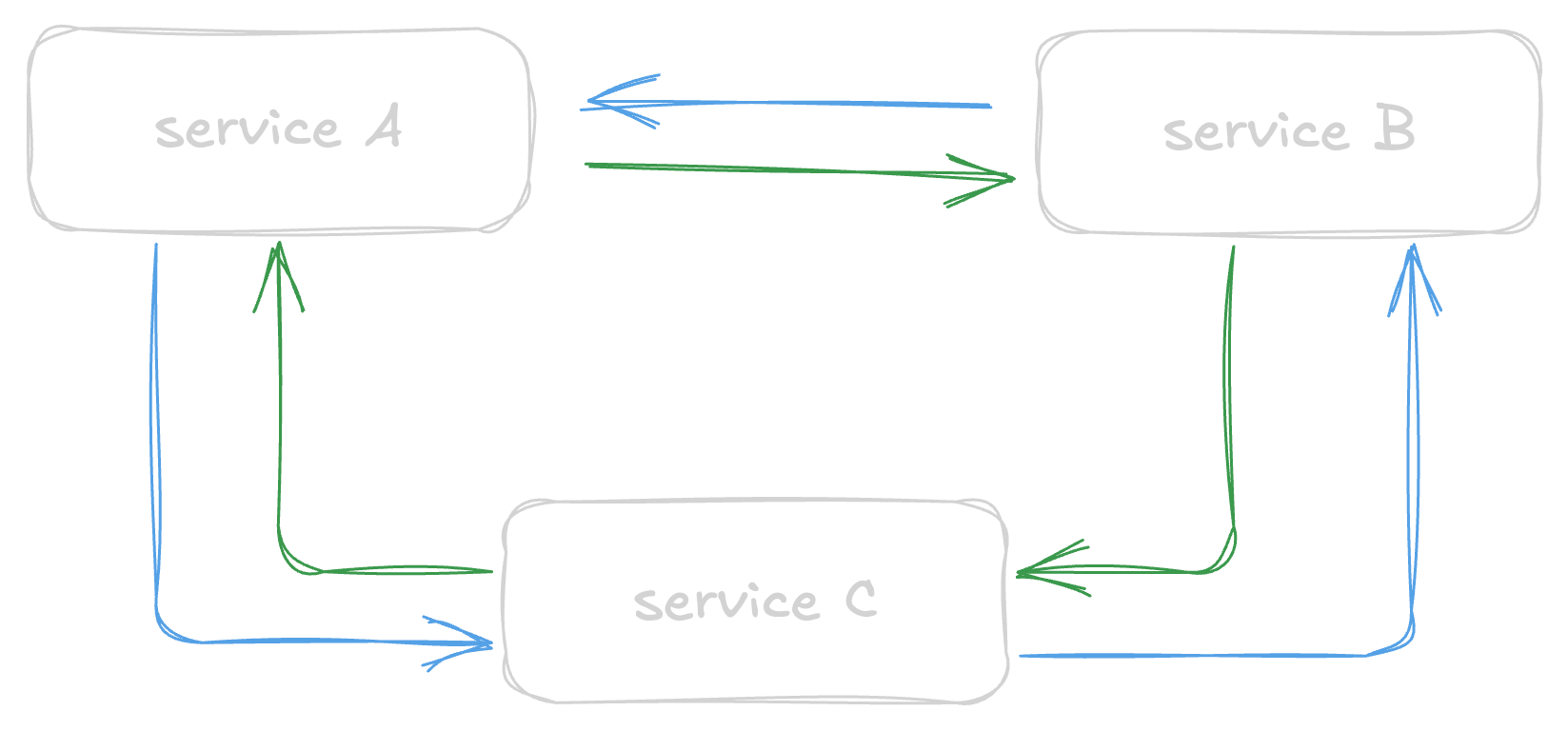
[!caution] Request-driven data passing is synchronous so if one service is down, requests are blocked
- Microservice architecture (==request-driven==)
- Data passing through real-time transport
- broker system, in memory storage to broker data
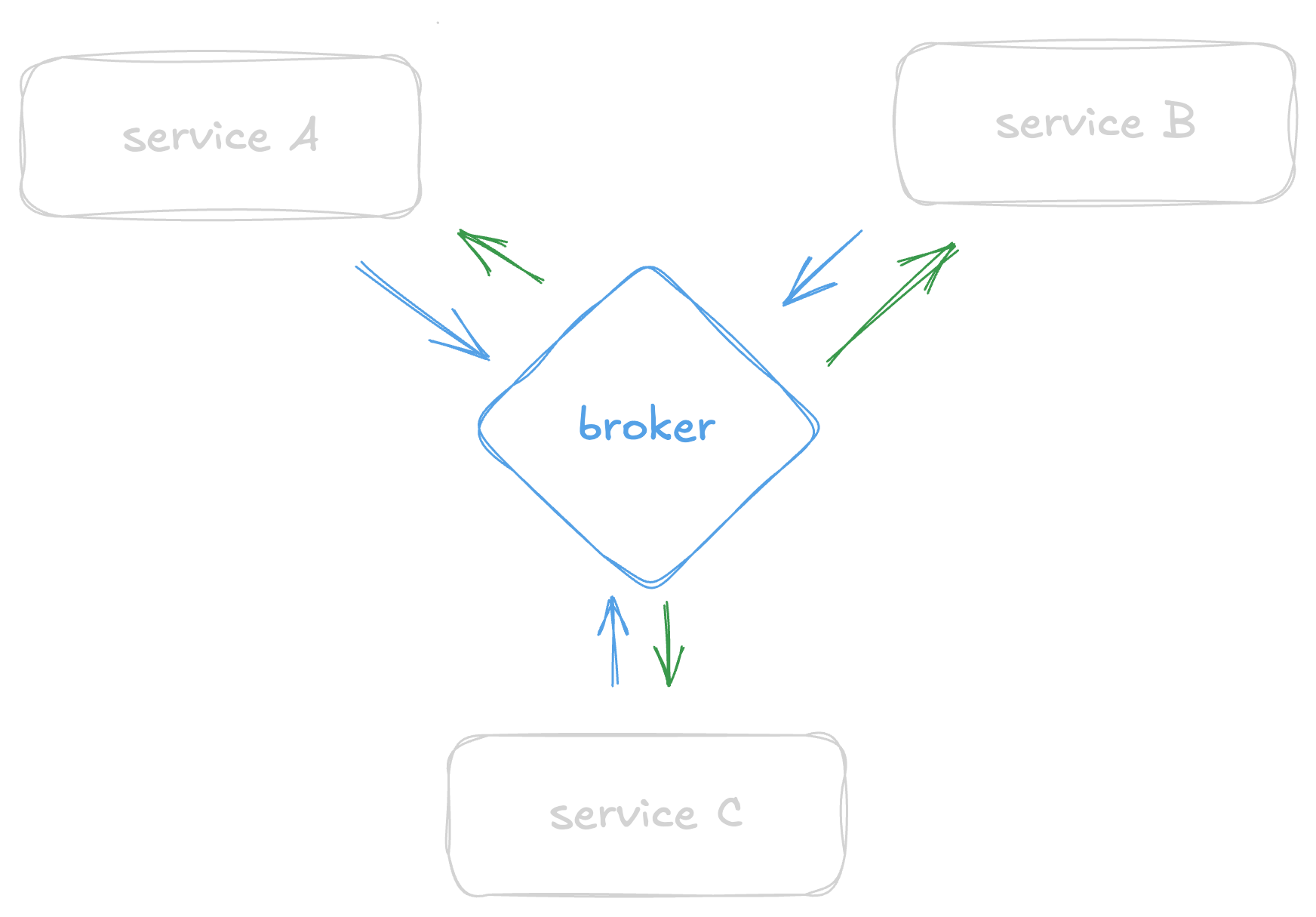
- named event-driven
- pubsub (Apache Kafka, Amazon Kinesis) & queue (Apache RocketMQ, RabbitMQ)
Batch Processing VS Stream Processing
- batch features also known has static features (Spark & MapReduce)
- streaming feature = dynamic features (Apache Flink, KSQL, Spark Streaming)